- Home
- FAQs
- Customer Video Gallery
- Customer Photo Gallery
- Bird Facts
- Bird Food Blog
- Bird Information
- Feeding Advice
- Small Animal Information
- A to Z of Guinea Pigs
- A to Z of Hamsters
- A to Z of Rabbits
- Basic Care for Guinea Pigs
- Basic Care for Hamsters
- Basic Care for Rabbits
- Basic care for Chinchillas
- Basic care for Ferrets
- Basic care for Gerbils
- Basic care for Mice
- Basic care for Rats
- Buying a Healthy Small Animal
- Does your Reptile need a Licence
- Equipment for Ferrets
- Equipment for Hamsters
- Equipment for Mice
- Equipment for your Chinchilla
- Equipment for your Gerbil
- Equipment for your Guinea Pig
- Equipment for your Rabbit
- Keeping a House Rabbit
- Dog Information
- Cat Information
- Customer Information
- Fat Balls
- Suet Pellets
- Straights
- Seed Mixes
- Suet Treats
- Mealworms
- Bird Feeders
- My Account
Birds Reproduction
Bird reproduction starts the same way as in mammals by the joining of an egg or ovum with a sperm cell in the oviduct. This fertilised ovum then forms the nucleus of the egg and the formation of the yolk, whites and shell can begin. The sperm from the male is transferred to the female when they touch cloaca, an act referred to as the cloacal kiss.
The first animals to develop the use of eggs with shells were the reptiles, in order that the egg would not dry out when not laid in water. With birds evolving from reptiles they have also made use of this incredible adaptation although they have taken it even further developing the egg into an amazing life support system for the growing embryo.
Most animals have two ovaries and oviducts, the passage for the egg to travel to the uterus. Birds however only have one and as the fertilised ovum travels down it a layer of albumen is applied around it, followed by the shell membranes. The shell itself is formed in the uterus where, depending on the movement of the egg, pigmentation forms patterns in the shell material.
An egg comprises several main elements, the yolk, the albumen, the membranes and the shell. The yolk is a fat rich food store with a small white spot, known as the germinal spot, and it is from here that the embryo begins to develop.
The whites of the egg, the albumen, supplies the embryo with water, provides some shock protection and helps gases to move in and out of the egg during development.
The membranes are three in number, one around the yolk known as the vitelline membrane, and two around the albumen, the inner and outer shell membranes. They provide a barrier against bacterial penetration and the air sac or air cell forms between the two shell membranes.
The shell is comprised of protein fibres and calcium carbonate or chalk merged into a complex mesh like structure and despite its smooth appearance is permeable to gases. It allows oxygen through to the growing embryo and waste gases and moisture to escape the egg. As the embryo develops the air sac increases in size and allows the mature chick its first breath.
There are also two twisted strands in the albumen attached to the yolk, called the chalaza, which hold the yolk in place and suspend the growing embryo in safety.
The yolk and albumen provide much for the developing embryo and all it needs from the outside world is oxygen and warmth.
The shape of most eggs is, obviously, egg shaped, but there are those that are adapted to suit particular circumstances. As an example cliff nesting birds have more pointed eggs, which makes them roll in a tight circle so they don’t fall off the cliff if disturbed.
The timing and number of clutches of eggs produced by different species varies dependent upon circumstances. The Blue Tit, for instance, feed their young mainly on insect larvae and so tend to produce one large clutch in early summer when this food source is more abundant. Conversely the Blackbird will lay two or three smaller clutches as they have a more abundant, steady food source and therefore have longer to raise multiple clutches.
Both of these situations however still share the same incubation behaviour. The female will lay one egg per day until the clutch is complete and it is only at this point that incubation starts. Even though the eggs may have different ages, this method of incubation results in all the young hatching around the same time and all have an equal chance at feeding time and for survival.
Some species such as birds of prey as well as others lay eggs two or three days apart and start incubation as soon as the egg is laid. This means that the young hatch at different intervals and when food is scarce the youngest hatchlings will not be able to compete for food and will not survive. In hard times such as this these fatalities will even become food for its erstwhile brothers and sisters and although this seems a bit gruesome after all the effort invested in breeding it helps prevent all the chicks being lost in harsh conditions.
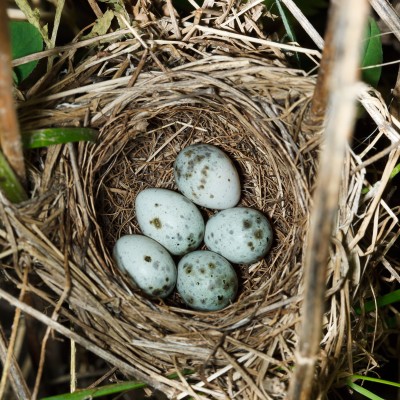
The colour of the eggs varies with different species and nesting habits. Birds that build their nests in holes tend to have light coloured eggs, white or blue, that are easier to locate in dark conditions and so avoid accidental damage. The hidden nature of the nesting site provides the camouflage. Ground laying birds, such as plovers, produce highly camouflaged eggs to prevent. Although Cuckoos already produce variably coloured and patterned eggs they do have the ability to mimic the appearance of other species eggs.

In most cases it is the female parent that incubates the eggs and to help transfer heat effectively she will develop a brood patch as the breeding season approaches. This brood patch has an area of skin with densely packed blood vessels and hardly any feathers, which produces more heat, due to the blood vessels, and this is transferred more easily to the egg due to the lack of feathers. Eggs are also turned periodically to ensure an even distribution of warmth. In species where the males also incubate eggs they will also develop a brood patch but they spend much less time at this than females. In all cases, however, the brood patch will disappear at the end of the breeding season.
It is possible that a developed chick may be able to communicate with its parent a day or two before hatching by answering its parents call with some vocal sounds. It will then start to use the hard tip of its bill, called the egg-tooth, to break out of the egg by laying on its back and pushing the egg-tooth into the shell above it. Once it has weakened the shell enough it will try to push the two halves of the eggshell apart. This may take a few days to accomplish and after a few days of hatching, the young lose the egg-tooth.
Hatchlings fall into two main categories, nidicolous and nidifugous. Nidicolous hatchlings are practically helpless, blind and naked, are wholly dependent on their parents and do not leave the nest until fledged. They tend to belong to species with the shorter incubation such as Blue Tit.
Nidifugous hatchlings are born with a covering of downy feathers and are able the leave the nest and fend for themselves. Many species of duck, Moorhen and Coot have nidifugous young.
Juvenile birds are those that have developed their first flight feathers and are able to leave the nest and fend for themselves. They may look very much like their parents, as in the Wren, or may be considerably different, as in the Robin.
It is against the law in the UK to disturb wild birds or their eggs, punishable by fines and even imprisonment. There are individuals who collect eggs but this is wholly illegal, not to mention immoral and destructive.
Egg Formation
The first animals to develop the use of eggs with shells were the reptiles, in order that the egg would not dry out when not laid in water. With birds evolving from reptiles they have also made use of this incredible adaptation although they have taken it even further developing the egg into an amazing life support system for the growing embryo.
Most animals have two ovaries and oviducts, the passage for the egg to travel to the uterus. Birds however only have one and as the fertilised ovum travels down it a layer of albumen is applied around it, followed by the shell membranes. The shell itself is formed in the uterus where, depending on the movement of the egg, pigmentation forms patterns in the shell material.
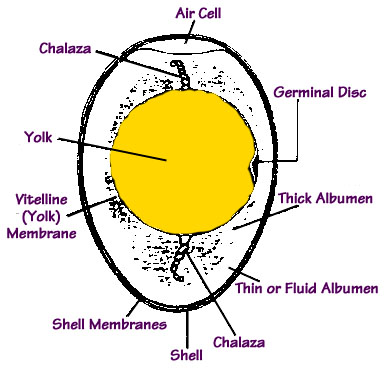
Egg Structure
An egg comprises several main elements, the yolk, the albumen, the membranes and the shell. The yolk is a fat rich food store with a small white spot, known as the germinal spot, and it is from here that the embryo begins to develop.
The whites of the egg, the albumen, supplies the embryo with water, provides some shock protection and helps gases to move in and out of the egg during development.
The membranes are three in number, one around the yolk known as the vitelline membrane, and two around the albumen, the inner and outer shell membranes. They provide a barrier against bacterial penetration and the air sac or air cell forms between the two shell membranes.
The shell is comprised of protein fibres and calcium carbonate or chalk merged into a complex mesh like structure and despite its smooth appearance is permeable to gases. It allows oxygen through to the growing embryo and waste gases and moisture to escape the egg. As the embryo develops the air sac increases in size and allows the mature chick its first breath.
There are also two twisted strands in the albumen attached to the yolk, called the chalaza, which hold the yolk in place and suspend the growing embryo in safety.
The yolk and albumen provide much for the developing embryo and all it needs from the outside world is oxygen and warmth.
The shape of most eggs is, obviously, egg shaped, but there are those that are adapted to suit particular circumstances. As an example cliff nesting birds have more pointed eggs, which makes them roll in a tight circle so they don’t fall off the cliff if disturbed.
Laying schedule
The timing and number of clutches of eggs produced by different species varies dependent upon circumstances. The Blue Tit, for instance, feed their young mainly on insect larvae and so tend to produce one large clutch in early summer when this food source is more abundant. Conversely the Blackbird will lay two or three smaller clutches as they have a more abundant, steady food source and therefore have longer to raise multiple clutches.
Both of these situations however still share the same incubation behaviour. The female will lay one egg per day until the clutch is complete and it is only at this point that incubation starts. Even though the eggs may have different ages, this method of incubation results in all the young hatching around the same time and all have an equal chance at feeding time and for survival.
Some species such as birds of prey as well as others lay eggs two or three days apart and start incubation as soon as the egg is laid. This means that the young hatch at different intervals and when food is scarce the youngest hatchlings will not be able to compete for food and will not survive. In hard times such as this these fatalities will even become food for its erstwhile brothers and sisters and although this seems a bit gruesome after all the effort invested in breeding it helps prevent all the chicks being lost in harsh conditions.
Camouflage
The colour of the eggs varies with different species and nesting habits. Birds that build their nests in holes tend to have light coloured eggs, white or blue, that are easier to locate in dark conditions and so avoid accidental damage. The hidden nature of the nesting site provides the camouflage. Ground laying birds, such as plovers, produce highly camouflaged eggs to prevent. Although Cuckoos already produce variably coloured and patterned eggs they do have the ability to mimic the appearance of other species eggs.

Incubation
In most cases it is the female parent that incubates the eggs and to help transfer heat effectively she will develop a brood patch as the breeding season approaches. This brood patch has an area of skin with densely packed blood vessels and hardly any feathers, which produces more heat, due to the blood vessels, and this is transferred more easily to the egg due to the lack of feathers. Eggs are also turned periodically to ensure an even distribution of warmth. In species where the males also incubate eggs they will also develop a brood patch but they spend much less time at this than females. In all cases, however, the brood patch will disappear at the end of the breeding season.
Hatching
It is possible that a developed chick may be able to communicate with its parent a day or two before hatching by answering its parents call with some vocal sounds. It will then start to use the hard tip of its bill, called the egg-tooth, to break out of the egg by laying on its back and pushing the egg-tooth into the shell above it. Once it has weakened the shell enough it will try to push the two halves of the eggshell apart. This may take a few days to accomplish and after a few days of hatching, the young lose the egg-tooth.
Nestlings
Hatchlings fall into two main categories, nidicolous and nidifugous. Nidicolous hatchlings are practically helpless, blind and naked, are wholly dependent on their parents and do not leave the nest until fledged. They tend to belong to species with the shorter incubation such as Blue Tit.
Nidifugous hatchlings are born with a covering of downy feathers and are able the leave the nest and fend for themselves. Many species of duck, Moorhen and Coot have nidifugous young.
Juveniles
Juvenile birds are those that have developed their first flight feathers and are able to leave the nest and fend for themselves. They may look very much like their parents, as in the Wren, or may be considerably different, as in the Robin.
Disturbing Birds
It is against the law in the UK to disturb wild birds or their eggs, punishable by fines and even imprisonment. There are individuals who collect eggs but this is wholly illegal, not to mention immoral and destructive.




